A cracked exhaust manifold can be a serious headache- noisy rides and reduced engine efficiency. But do you need to replace it right away, or is welding an option? With the right approach, welding could save your manifold and your wallet. Here’s how.
Can You Weld a Cracked Exhaust Manifold?
A cracked exhaust manifold can be welded, but success depends on the material and size of the crack. Preheating and slow cooling are necessary for cast iron. While welding is a cost-effective repair, replacement is sometimes required for larger or recurring cracks.
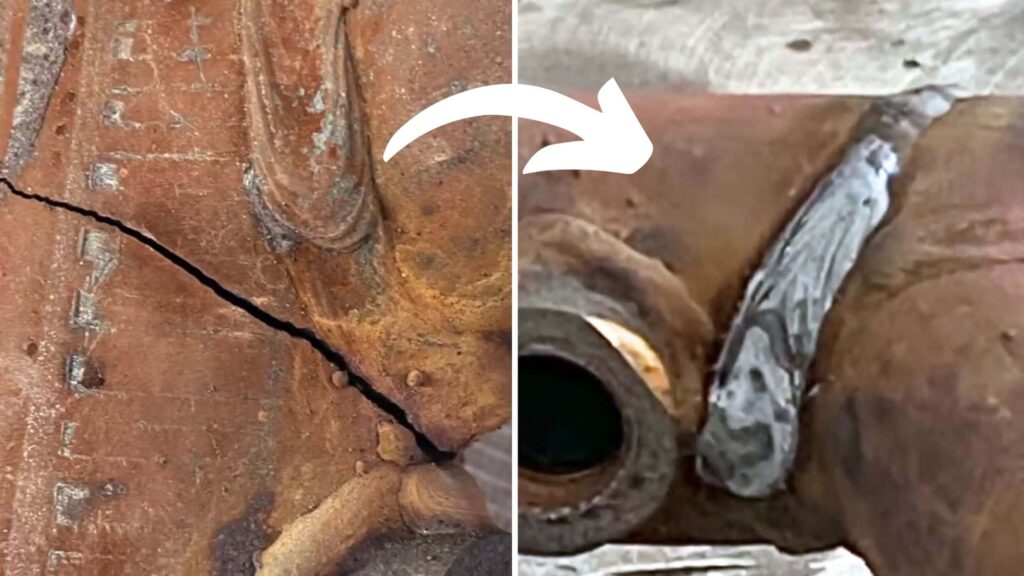

Table Of Content
- What causes exhaust manifolds to crack?
- What happens if I don’t repair a cracked exhaust manifold?
- Which type of Welding Is Best For An Exhaust Manifold?
- How to Weld a Cracked Exhaust Manifold
- Alternatives to Welding a Cracked Exhaust Manifold
- How can I prevent future cracks in my exhaust manifold?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What causes exhaust manifolds to crack?
Exhaust manifolds crack primarily due to the intense heat and stress they endure during engine operation. Rapid temperature changes cause the metal to expand and contract, creating thermal stress. Over time, this stress weakens the manifold, leading to cracks.
Other factors include:
Vibration: Constant engine vibrations, especially in poorly mounted or ageing engines, can cause the manifold to develop stress fractures.
Poor Material Quality: Low-quality materials, such as inferior cast iron, are more prone to cracking due to their inability to withstand high temperatures and pressure.
Exhaust Leaks: A small exhaust leak near the manifold can increase temperatures in that area, creating a hotspot and leading to localized cracking.
Improper Installation: If the manifold is incorrectly bolted or over-tightened, it may not expand and contract evenly, increasing the chance of cracking over time.
What happens if I don’t repair a cracked exhaust manifold?
If you don’t repair, several issues can arise:
- Engine Performance Drops: A cracked manifold can disrupt the exhaust flow, causing a loss of engine power and decreased fuel efficiency. You may notice sluggish acceleration or rough idling.
- Loud Noises: Cracks often result in loud ticking or hissing noises as exhaust gases escape. This can become more noticeable as the crack worsens.
- Increased Emissions: Exhaust gases can leak before reaching the catalytic converter, leading to higher emissions and possibly causing your vehicle to fail emission tests.
- Exhaust Fumes in the Cabin: Harmful gases like carbon monoxide can leak into the vehicle’s interior, posing a serious health risk to you and your passengers.
- Worsening Damage: Ignoring a cracked exhaust manifold can lead to further deterioration of the part, making it harder or impossible to repair. Over time, it can also damage other engine components due to increased pressure or heat.
Is Welding a Cracked Exhaust Manifold a Permanent Fix?
Welding a cracked exhaust manifold can be a permanent fix if done correctly. However, it depends on the extent of the damage and the quality of the weld. If the manifold is severely weakened or the underlying issues aren’t addressed, cracks may reappear over time.
Which type of Welding Is Best For An Exhaust Manifold?

The best type of welding for an exhaust manifold largely depends on the material of the manifold. Here are the top welding methods:
- TIG Welding (Tungsten Inert Gas Welding) is generally the best option for exhaust manifolds, especially those made from stainless steel. It allows for precise, clean welds with good heat control, which is crucial when working with thin or heat-sensitive materials like an exhaust manifold.
- MIG Welding (Metal Inert Gas Welding): MIG welding is another good option, particularly for mild steel manifolds. It’s easier to use than TIG and works well for larger cracks, but it can produce less precision than TIG welding.
- Stick Welding (Shielded Metal Arc Welding): Stick welding with nickel-based electrodes is often used for cast iron manifolds. Cast iron is tricky to weld, and if done properly with preheating and slow cooling, stick welding allows for strong, durable joints.
For most situations, TIG welding is preferred because of its precision and clean results, especially on high-heat components like exhaust manifolds. However, the specific material of the manifold should guide your choice of welding technique.
Can a Rusty Exhaust Manifold be Welded?
Yes, a rusty exhaust manifold can be welded, but it requires thorough cleaning first. Remove any rust and debris from the welding area using a wire brush or grinder to ensure a strong bond. If the rust is extensive, it may compromise the integrity of the exhaust, making replacement a better option.
How to Weld a Cracked Exhaust Manifold
Follow these steps for an effective fix:
1. Gather Tools and Materials
- Welding machine (TIG, MIG, or Stick, depending on the material)
- Nickel-based welding rods (for cast iron)
- Stainless steel filler rods (for stainless steel manifolds)
- Grinder
- Safety gear (welding mask, gloves, and protective clothing)
- Preheating tool (for cast iron manifolds)
- Cleaning brush and degreaser
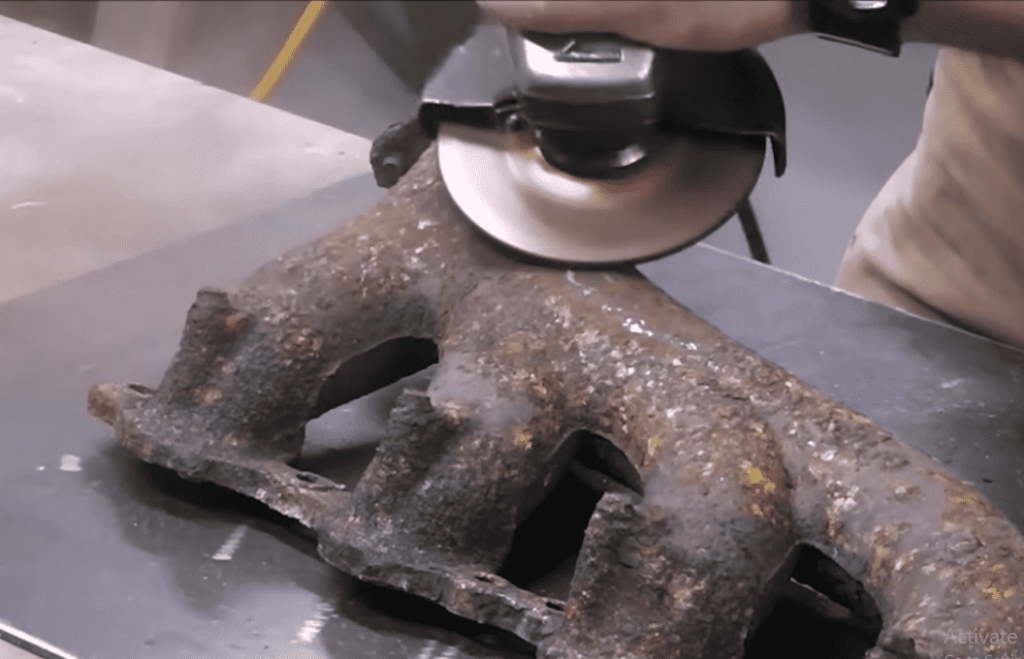
2. Prepare the Manifold
- Remove the manifold from the vehicle to get better access and avoid damaging other components.
- Clean the manifold thoroughly, using a wire brush and degreaser to remove dirt, rust, or oil. A clean surface ensures a stronger weld.
- Grind the crack lightly to expose fresh metal and remove any brittle edges. This also helps create a smoother surface for welding.

3. Preheat the Manifold (for Cast Iron)
- Preheating is crucial for cast iron manifolds to avoid further cracking. Use a propane torch to gradually heat the manifold to around 500°F (260°C).
- This helps reduce thermal stress when you start welding.

4. Weld the Crack
- TIG Welding: Ideal for precise, clean welds, especially on stainless steel manifolds. Slowly work along the crack, ensuring even heat distribution.
- MIG Welding: Works well for mild steel. Ensure even passes and steady speed to avoid overheating.
- Stick Welding (for Cast Iron): Use nickel-based electrodes to fill the crack. Keep the weld bead small to reduce stress on the cast iron, and maintain a steady hand to prevent overheating.
5. Cool Down Gradually
- After welding, it’s important to cool the manifold slowly to avoid new cracks. Cover the manifold in a heat-resistant blanket or allow it to cool in the air gradually. Avoid rapid cooling, which can cause stress and weaken the repair.
6. Grind and Finish
- Once the manifold has cooled, grind the weld smoothly. This improves the airflow and helps prevent any stress points that could cause future cracks.
7. Reinstall the Manifold
- After inspecting the weld for any remaining cracks or weak spots, reinstall the manifold on the vehicle.
- Double-check for proper sealing to prevent exhaust leaks.
Can I weld the exhaust manifold while still attached to the engine?
Welding an exhaust manifold while still attached to the engine is not recommended. The heat from welding can damage nearby components, and accessing the crack properly becomes difficult. Removing the manifold ensures a safer, cleaner, and more effective weld.
Alternatives to Welding a Cracked Exhaust Manifold
- Exhaust Manifold Sealants: High-temperature exhaust sealants can temporarily seal small cracks. These are easy to apply and can hold up under moderate heat, but they’re only a short-term fix.
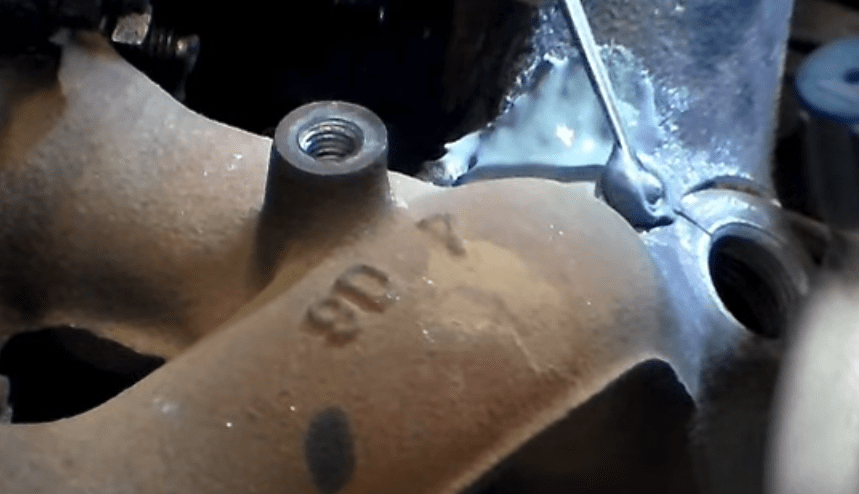

- Exhaust Repair Clamps: For minor cracks, an exhaust repair clamp can cover and seal the damage. While not a permanent solution, it can work for some time until a proper fix is arranged.
- Replace the Exhaust Manifold: When the crack is extensive or the manifold is severely damaged, replacing it is often the best long-term solution. Although more expensive, it eliminates the risk of further problems.
- Exhaust Wraps or Patches: Exhaust wraps made from heat-resistant materials can be used to wrap small cracks. Similarly, metal patches can be clamped or welded over the damaged area for a more durable repair.
These alternatives can provide temporary relief, but a proper weld or replacement is usually needed for a lasting solution.
Can JB Weld or other high-temperature epoxies fix a cracked manifold?
JB Weld or other high-temperature epoxies can temporarily fix small cracks in an exhaust manifold. However, due to the extreme heat and pressure the manifold endures, these fixes are not permanent and may eventually fail. Welding or replacement is usually a more durable solution.
How can I prevent future cracks in my exhaust manifold?
Preventing future cracks involves taking a few proactive steps:
- Regular Inspections: Routinely check the exhaust manifold for signs of wear, rust, or small cracks. Catching damage early can prevent it from worsening.
- Proper Installation: Ensure the manifold is installed correctly, with bolts tightened to the recommended torque. Over-tightening can create stress points, leading to cracks.
- Address Exhaust Leaks Promptly: If you notice an exhaust leak, repair it immediately. Leaks increase the temperature around the manifold, creating hot spots that can cause cracking.
- Use Heat Shields or Wraps: Installing heat shields or exhaust wraps can help distribute heat more evenly, reducing thermal stress on the manifold.
- Allow the Engine to Warm Up Gradually: Avoid sudden, extreme temperature changes by letting your engine warm up slowly before driving. This reduces thermal expansion and contraction which can crack the manifold.
- Use High-Quality Parts: Opt for exhaust manifolds made from durable materials like stainless steel, which are more resistant to heat and stress.
Frequently Asked Questions
1) Do I need to preheat the manifold before welding?
Yes, preheating the manifold before welding is recommended, especially for cast iron. Preheating helps reduce thermal stress, minimizes the risk of cracking, and allows for better penetration of the weld. Aim for a temperature of around 500°F (260°C) before starting the welding process.
2) Can a welded manifold crack again?
Yes, a welded manifold can crack again. Factors like excessive heat, stress from vibrations, or improper welding techniques can lead to new cracks forming at the weld or in nearby areas. Regular inspections and maintenance are essential to catch any signs of cracking early and address them promptly.
3) Can you weld a cast iron exhaust manifold?
Yes, you can weld a cast iron exhaust manifold. Using nickel-based welding rods is recommended, as they help prevent cracking. Preheating the manifold is also crucial to reduce thermal stress.
4) Can you drive with a cracked exhaust manifold?
Yes, you can drive with a cracked exhaust manifold, but it’s not advisable. Doing so can lead to increased engine noise, reduced performance, and harmful exhaust gases leaking into the vehicle cabin, posing health risks. Additionally, it can cause further damage to the engine over time, so it’s best to repair it as soon as possible.
5) Can exhaust manifold cracks cause performance issues?
Yes, exhaust manifold cracks can cause performance issues. They can lead to exhaust leaks, which result in a loss of back pressure and reduced engine efficiency. This can manifest as decreased power, poor fuel economy, and increased emissions. Addressing any cracks promptly is essential to maintain optimal vehicle performance.
6) Can I use a propane torch to weld an exhaust manifold?
Using a propane torch to weld an exhaust manifold is not recommended. Propane typically doesn’t reach the high temperatures needed for effective welding, especially on materials like stainless steel or cast iron. For better results, use a TIG or MIG welder, which can achieve the necessary heat and provide a stronger, more durable weld.
7) What is the best filler material for welding stainless steel manifolds?
The best filler material for welding stainless steel manifolds is ER308L or ER316L stainless steel filler rods or wires. These materials are specifically designed for welding stainless steel and provide good corrosion resistance and strength. ER308L is ideal for most applications, while ER316L offers enhanced resistance to corrosion in harsh environments. Always choose a filler material that matches the composition of the manifold for optimal results.
Conclusion
Welding a cracked exhaust manifold can be a viable solution to extend its lifespan and maintain your vehicle’s performance. While it offers a durable fix when done correctly, it’s essential to consider factors such as the manifold material, the extent of the damage, and proper welding techniques. Regular inspections and maintenance can help prevent future cracks and ensure the longevity of your repair. If you’re not comfortable with welding or if the damage is significant, consulting a professional or considering a replacement may be the best route. By addressing cracks promptly and effectively, you can keep your engine running smoothly and efficiently.

